Top Analytical Methods for Herbal Substances by Leading OEM Manufacturers
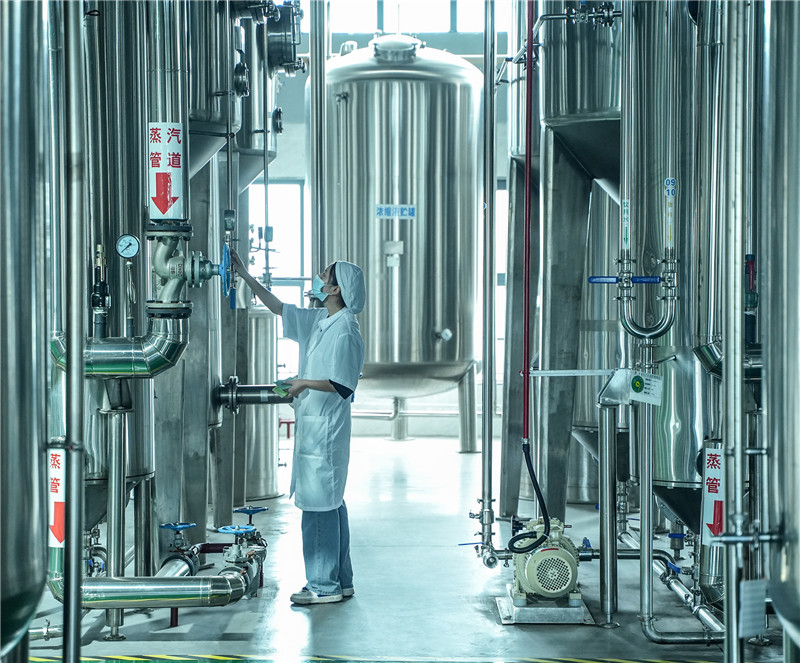
In the world of herbal substances, understanding the right analytical methods is crucial for quality control and product development. As a buyer, I appreciate working with OEM manufacturers who are dedicated to utilizing cutting-edge techniques that ensure the purity and efficacy of their herbal offerings. Our analytical methods cover a broad spectrum, from chromatography to spectrometry, providing reliable insights into composition and potency. I find that choosing the right manufacturer not only guarantees the authenticity of the product but also enhances my brand’s reputation in the market. Whether I’m interested in raw materials or finished products, partnering with experts who prioritize rigorous testing and compliance with industry standards is essential. Don’t compromise on quality—partner with those who truly understand the science behind herbal substances and can deliver exceptional results every time. This way, I can confidently meet the needs of my customers and stand out in a competitive landscape.
Analytical Methods For Herbal Substances Service Factory-Direct Excellence
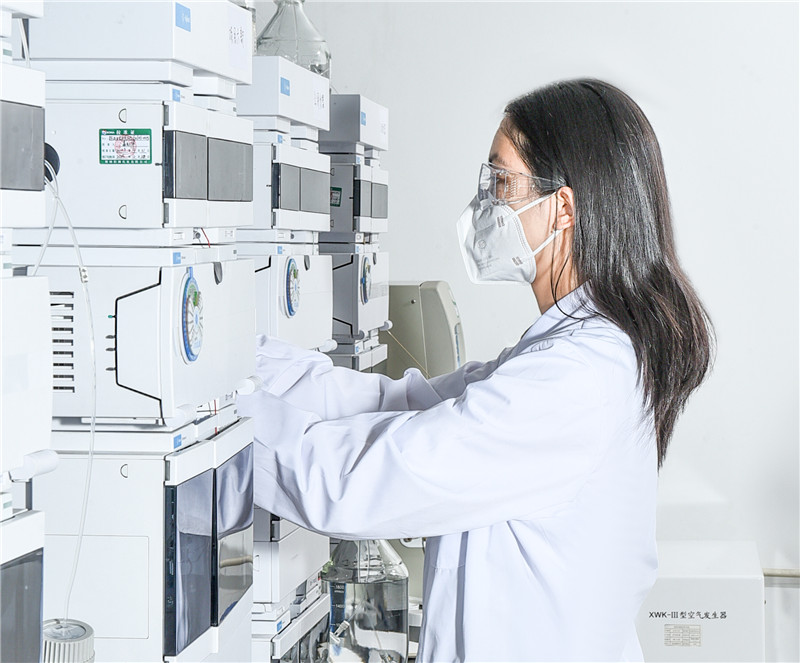
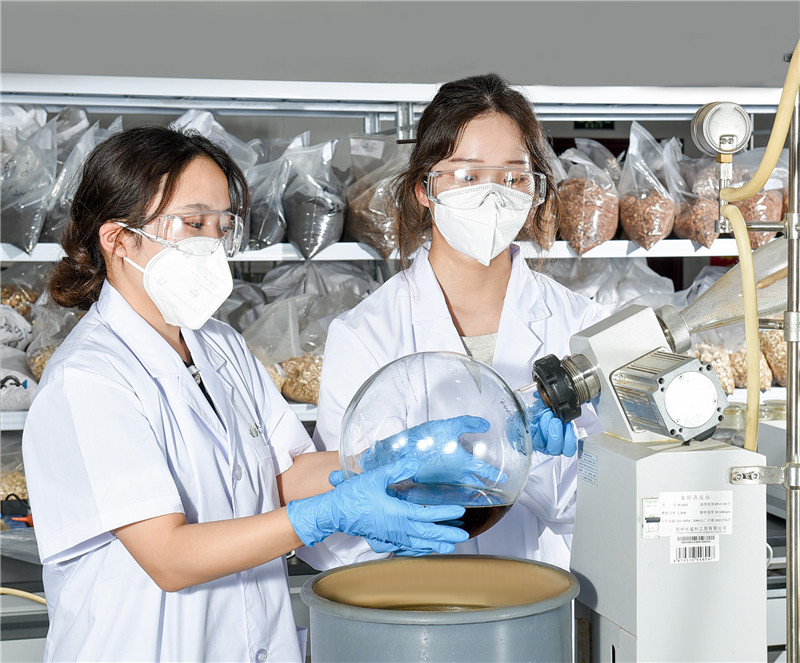
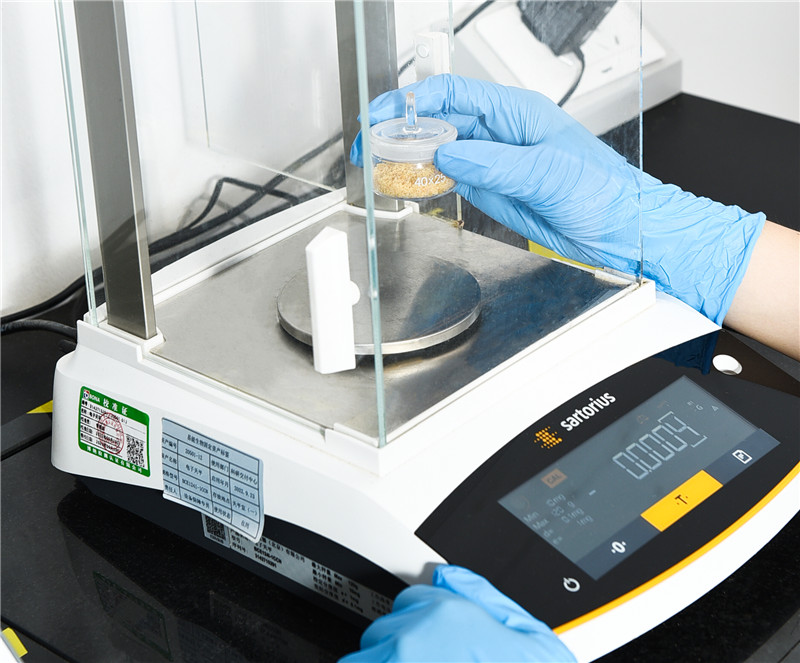
In the ever-evolving landscape of herbal products, ensuring quality and efficacy has become paramount for global buyers. Analytical methods play a crucial role in verifying the authenticity and potency of herbal substances. Conventional testing approaches often fall short, leading to variability and inconsistencies. As a result, investing in advanced analytical techniques allows producers to uphold quality standards, safeguard brand integrity, and meet market demands efficiently. Modern analytical methods encompass a range of techniques, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and various spectroscopic methods. These techniques not only enhance the identification and quantification of active compounds within herbal substances but also assist in detecting contaminants and adulterants. By implementing robust analytical protocols, manufacturers can provide greater transparency to their customers, thereby fostering trust and confidence in their products. In conclusion, a commitment to excellence through meticulous analytical methods offers a competitive edge in the herbal industry. Buyers seeking high-quality herbal substances should prioritize suppliers who embrace these advanced techniques, ensuring that they receive products that not only meet regulatory standards but also deliver authentic health benefits. As the global market grows, quality assurance through analytical excellence will remain a key differentiator for successful partnerships in the herbal sector.
Analytical Methods For Herbal Substances Service Factory-Direct Excellence
| Method Name | Description | Application | Sensitivity | Limit of Detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | A technique used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. | Used in the analysis of active compounds in herbal medicines. | High | 0.1 mg/L |
| Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) | Combines gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. | Useful for volatile and semi-volatile compounds in herbal extracts. | Very High | 1 ng/mL |
| Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) | A simple and cost-effective technique for identifying and separating non-volatile mixtures. | Used for qualitative analysis of herbal compounds. | Moderate | 50 mg/kg |
| Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) | A method that uses infrared light to analyze materials by their molecular vibrations. | Used for functional group identification in herbal compounds. | Moderate | 10 mg/sample |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy | A powerful technique used for determining the structure of organic compounds. | Ideal for detailed structural analysis of herbal substances. | Very High | 0.5% concentration |
Related Products